At SNAP Biolabs, we pride ourselves in helping our clients succeed in their research endeavors. We provide customized flow cytometry solutions and are looking forward to working with you to achieve your goals.
Immunophenotyping
Immunophenotyping is a tool used to profile immune cells in peripheral blood, tissues and tumor samples. SNAP Biolabs has extensive experience designing immunophenotyping panels, either standard panels or more complex panels that include activation markers, exhaustion markers, intracellular cytokines, and phosphorylation of intracellular proteins.
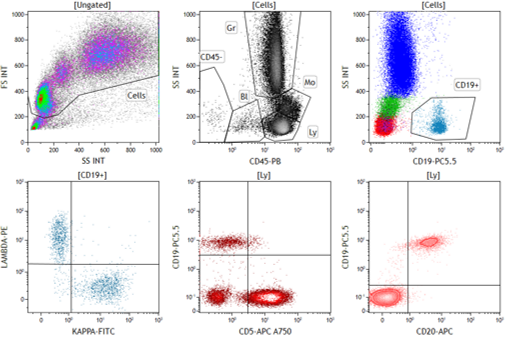
Gain new insight into your drug mechanism of action and PD through robust and in-depth immunophenotyping. Maximize immunotherapeutic benefits, limit unwanted toxicities, and increase your chances of preclinical/clinical success by comprehensively characterizing cells of interest. Use our high-quality flow cytometry data to better understand:
- The immune make-up of relevant organs such as tumors, blood, spleen, and lymph nodes
- Therapeutic effect on the frequencies and functionality of cell subsets
- Individual specimen variations and heterogeneity of response

SNAP Biolabs is pleased to offer the following immunophenotyping panels:
- Standard T cell, B Cell, and NK Panels
- Regulatory T cells
- Memory, Naïve, and Effector T cells
- TH1/H2/TH17/TH9T cells
- T cell activation/prolifiration
- Intracellular Cytokines
- Phospho pERK, pAKT, pSTAT1, pSTAT5
- Memory B cells and Plasma Cells
- Custom Immunophenotyping Panels
Receptor Occupancy
Flow cytometry can be a powerful tool for the evaluation of Receptor Occupancy (RO) to provide an assessment of the therapeutic binding to the target receptor. Evaluating RO during the development of new biologic drugs is crucial not only for candidate selection in the early stages but also to confirm that the therapeutic is binding to its cellular target and establishing the dose or plasma concentration needed to reach a therapeutically-effective receptor occupancy level when combined with pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic (PD) data.
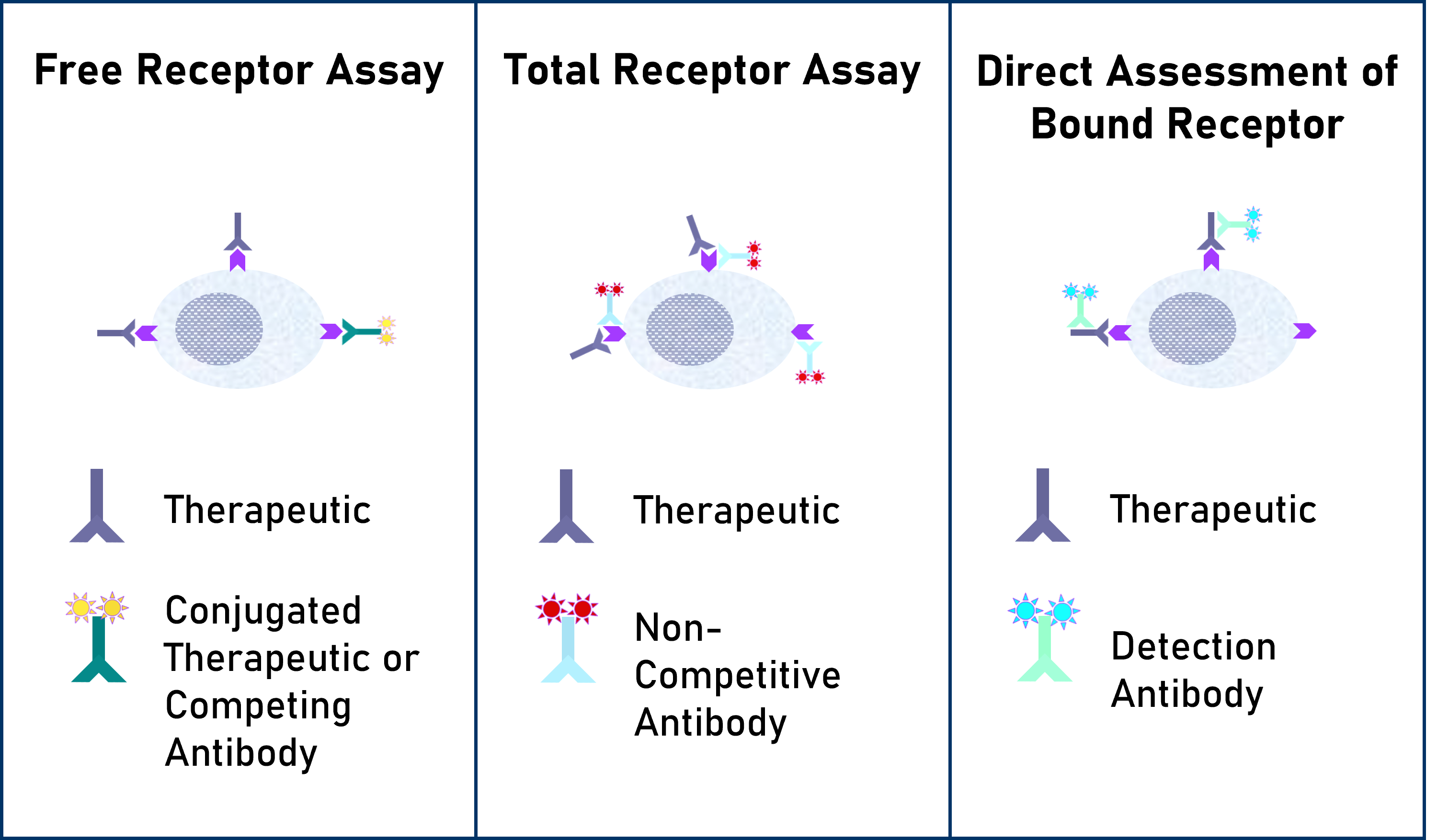
At SNAP Biolabs we provide custom-developed receptor occupancy assays based on client-defined parameters to identify the binding of a therapeutic compound to its specific target....
Flow Assessment of receptor occupancy by flow cytometry can take several approaches:
Free Receptor Assay– Shown in the Left Panel is an illustration of free receptors that are not occupied by a biotherapeutic agent detected using either a fluorescently labeled competitive antibody or biotherapeutic agent.
Free and Total Receptor Assay– Shown in the Middle Panel is an illustration of free and total receptor assay design which depicts the total receptors available, recognized by a non-competitive antibody bound to a different epitope on the receptor from the one recognized by the biotherapeutic agent. This design can be used to determine the ratio of free (unoccupied) sites to the total sites available.
Direct Assessment of Bound Receptor– Shown in the Right Panel is an illustration of direct assessment of bound receptor with a biotherapeutic agent, typically detected with a fluorescently labeled anti-drug antibody.
Our recommendations are based on the following resources:
- Receptor occupancy by flow cytometry. Litwin V, Green C, Stewart JJ. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2016; 90:108–109.
- Role of receptor occupancy assays by flow cytometry in drug development. Stewart JJ, Green CL, Jons N, Liang M, Xu Y, Wilkins DE, Moulard M, Czechowska K, Lanham D, McCloskey TW, Ferbas J, van der Strate BW, Högerkorp CM, Wyant T, Lackey A, Litwin V. Cytometry B Clin Cytom 2016; 90:110–116.
Cell Health and Integrity
Assessment of cell health is crucial in basic biomedical research, assay development and drug discovery.
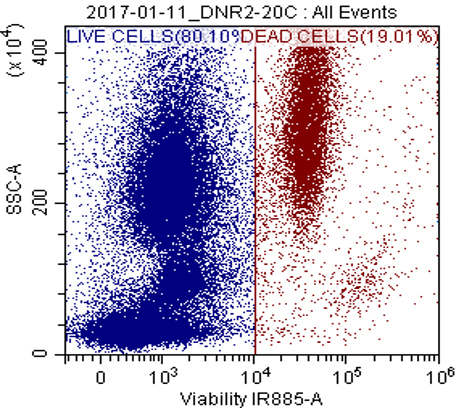
Viability Assay
This assay provides quantitative data regarding cell viability within a population, allowing researchers to assess the effects of various treatments, drugs, or experimental conditions on cell survival. Non-fixable and fixable viability dyes selected based on the panel design, e.g. PI, 7-AAD, ViaKrome, Hoechst 33342, DRAQ-5, DRAQ-7.
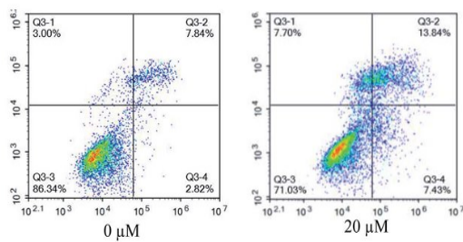
Apoptosis Assay
In early apoptosis, cells lose membrane phospholipid asymmetry, while the integrity of the cell membrane is maintained. Annexin-V in combination with PI or DAPI viability dye can show three different cell populations, live cells, necrotic or late apoptotic, and early apoptotic.
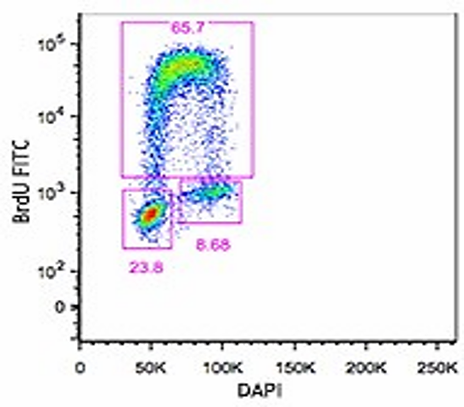
Proliferation Assay
The proliferation assay using flow cytometry provides valuable insights into cell behavior, including growth kinetics and cell cycle progression. During the S-phase of a cell cycle BrdU is a structural analog of thymidine incorporates into DNA and in conjunction with cell cycle dye can provide a measure of proliferation.
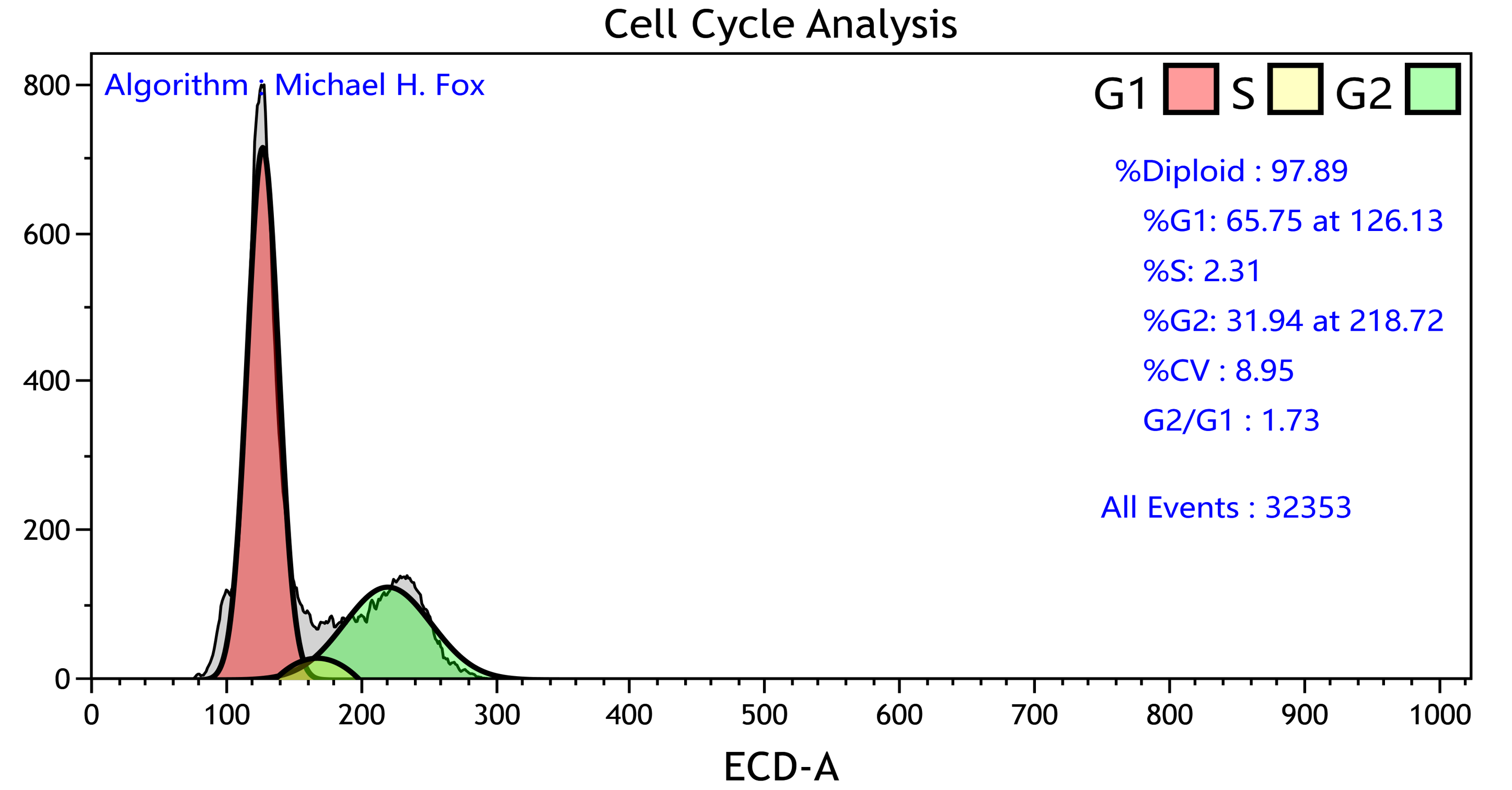
Cell Cycle Assay
Detection of the cells in the different stages of division through a change in DNA content with fluorescent DNA binding dyes, e.g. Propidium Iodide and DAPI.
Flow Cytometry in ADC Antibody Selection
Flow cytometry is an essential tool in Antibody Drug Conjugate (ADC) development. It allows precise characterization and selection of antibodies capable of delivering cytotoxic payloads to target cancer cells effectively.
Flow cytometry allows researchers to assess binding kinetics, determine antigen expression levels, and evaluate internalization rates of ADCs, providing invaluable data for optimizing ADC design and enhancing their therapeutic efficacy. Moreover, this technology facilitates the screening of ADC components and enables the monitoring of cellular responses to ADC treatments, ultimately contributing to the development of more potent and targeted cancer therapies.
At SNAP Biolabs, we developed methods and assays to measure and assess antigen binding, internalization, and cell-specific cytotoxicities. All our assays are adaptable to fit your experimental needs.
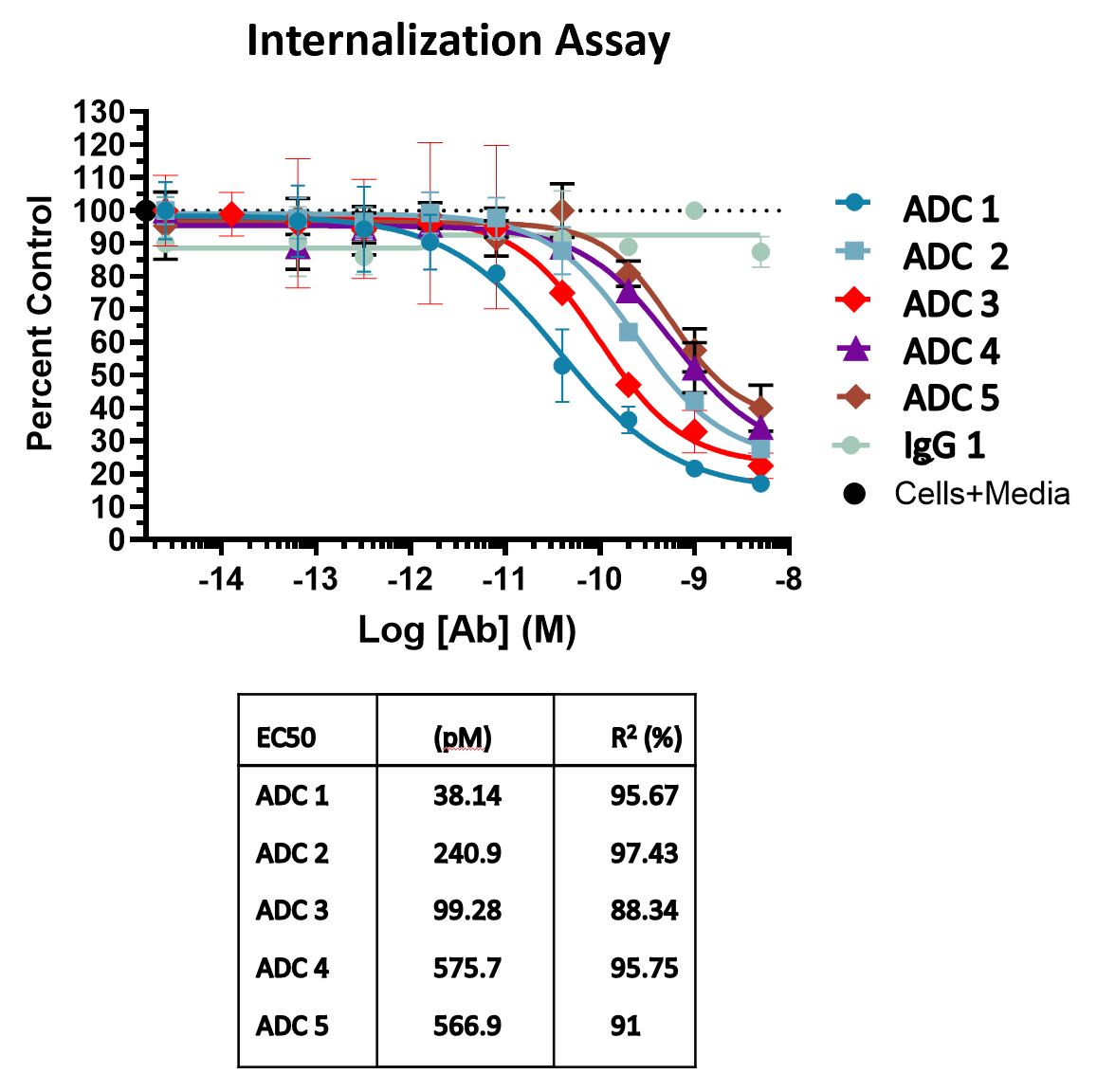
Internalization Assays using Toxin-conjugated Reagents
Generation of immunotoxins by linking Anti-Tumor Antigens monoclonal antibodies to the ribosome-inactivating protein toxin Saporin.
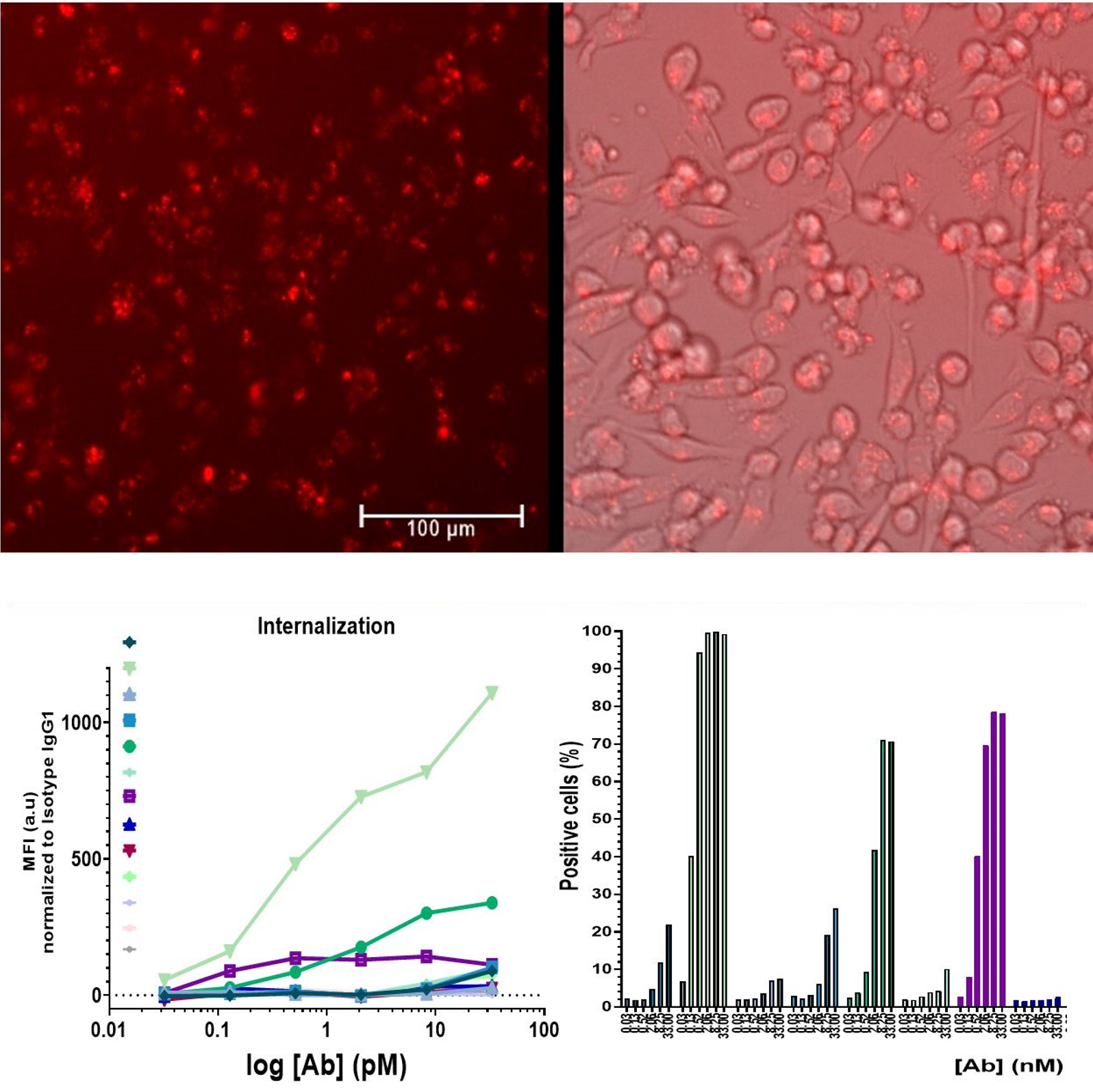
Internalization Assay Using pH-Sensitive Reagents
The internalization process of Antibody Drug Conjugates (ADCs) is crucial for delivering the small molecule toxin to its target inside cells, primarily occurring through receptor-mediated endocytosis. The assay involves conjugating antibodies with a pH-sensitive dye that remains non-fluorescent in the extracellular environment and becomes fluorescent at low lysosomal pH. Detecting fluorescence indicates successful internalization of the antibody. This fluorescence is quantitatively measured using flow cytometry. The assay outcome reveals a dose-dependent rise in the percentage of fluorescent cells compared to those treated with isotype control, providing a reliable indicator of ADC internalization efficacy.
